| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | ||||
| 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
| 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 |
| 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 |
| 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 | 29 | 30 | 31 |
- 구현
- VCS
- BFS
- Java
- graph
- heap
- 광연자동차운전면허학원
- hash
- Union Find
- SinglyLinkedList
- array
- DailyLeetCoding
- Easy
- sorting
- leetcode
- greedy
- hash table
- Leedcode
- Medium
- python3
- A* Algorithm
- stack
- Two Pointers
- ArrayList vs LinkedList
- Bellman-Ford
- Hashtable
- String
- LinkedList
- dfs
- 자료구조
- Today
- Total
Min IT's Devlog
[python3] 1254. Number of Closed Islands 본문
풀이 일자: 23.04.06
난이도: [Medium]
분류: [Array, DFS, BFS, Union Find]

문제 내용

문제의 내용은 0(land), 1(water)로 이루어진 배열이 주어졌을 때 사면이 물로 둘러싸여있는 섬의 수를 구하는 문제였다.
문제 해결 흐름
1. 일단 가장 먼저 떠오른 방법은 Union-Find이긴 했다.
→ 1의 group과 0의 group으로 나눠질거고 0내부에서도 각 섬별로 grouping이 되는거니까 Union-Find로도 가능하다.
2. Union-Find는 간단하지만 더 쉬운 방법을 찾아볼 필요가 있다. DP나 DFS정도를 생각할 수 있겠다.
→ DP는 점화식을 뽑아야 하는데 그것보다는 더 쉬운 방법일 수 있는 DFS를 선택하자.
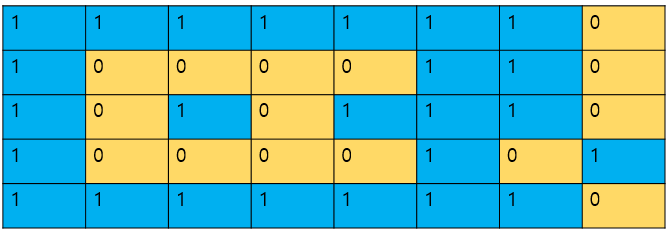
3. 우선 edge에 0이 등장한다는 건 거기는 island가 아닌 단순한 육지이기 때문에 edge쪽에 존재하는 0의 group들을 모두 1(물)로 육지를 뒤덮어버리자.
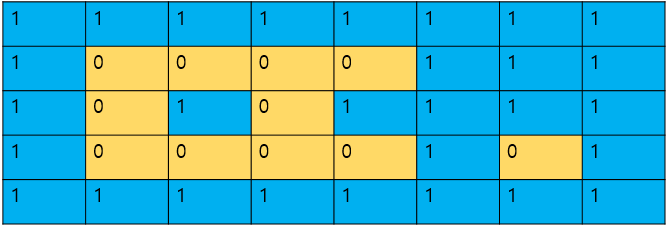
4. 남은 0들은 모두 섬을 구성하는 land로 보면 되므로 grid배열을 순회하면서 이것도 물로 채워버리면 된다.
→ 물로 채우는 recursive 함수가 끝날 때마다 하나의 섬을 다 물로 채운 것이므로 ans += 1을 해주면 된다.
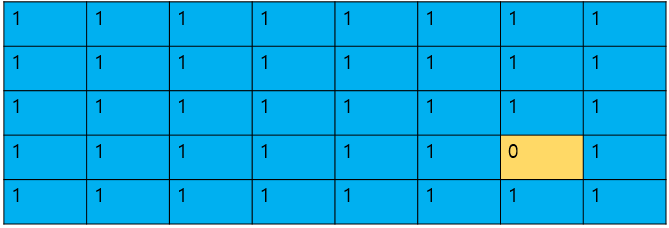
class Solution:
def waterfill(self, x, y): // 물을 채우는 공통 함수
if 0<=x and x<=len(self.grid)-1 and 0 <=y and y <=len(self.grid[0])-1:
if self.grid[x][y] == 0:
self.grid[x][y] = 1;
self.waterfill(x-1,y);
self.waterfill(x+1,y);
self.waterfill(x,y-1);
self.waterfill(x,y+1);
def closedIsland(self, grid: List[List[int]]) -> int:
self.grid = grid;
w, h = len(grid[0]), len(grid);
ans = 0;
for i in range(h): //edge부분이 0인 경우 육지이므로 그냥 물로 채우기
if i == 0 or i == h - 1:
for j in range(w):
self.waterfill(i,j);
else:
self.waterfill(i,0);
self.waterfill(i,len(grid[0])-1);
for i in range(1, h): // 나머지는 모두 섬으로 섬 하나씩 물을 채우기
for j in range(1, w - 1):
if self.grid[i][j] == 0:
self.waterfill(i,j);
ans += 1; // 섬 하나 채울 때마다 ans += 1
return ans;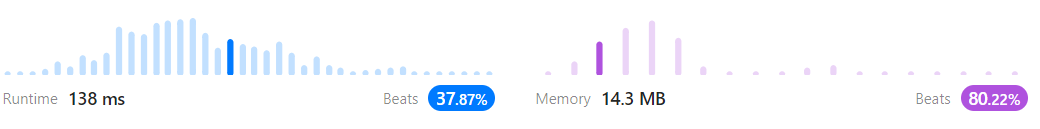
Time Complexity: O(wh)
grid라는 배열을 순회하기 때문에 해당 배열의 크기 만큼의 시간복잡도가 발생할 것이며 추가적으로 함수의 recursion이 일어나기에 조금 더 복잡할 것이다.
Space Complexity: O(wh)
수월한 코딩을 위해 grid를 멤버변수로 저장해서 변형했기 때문에 배열의 크기만큼의 공간복잡도 + recursion으로 인한 추가적인 공간복잡도가 나올 것이다.
다른 해결 방식
1. 같은 DFS방식으로 풀었는데 좀더 간결하고 빠르게 푼 user가 있었다.
class Solution:
def closedIsland(self, grid: List[List[int]]) -> int:
rows, cols = len(grid), len(grid[0])
count = 0
def dfs(i, j):
if i < 0 or j < 0 or i >= rows or j >= cols:
return False
if grid[i][j] == 1:
return True
grid[i][j] = 1 # mark as visited
left = dfs(i, j-1)
right = dfs(i, j+1)
up = dfs(i-1, j)
down = dfs(i+1, j)
return left and right and up and down
for i in range(rows):
for j in range(cols):
if grid[i][j] == 0 and dfs(i, j):
count += 1
return count
2.처음에 떠올렸던 Union-Find에 대한 풀이도 있었다.
class UnionFind: #일반적인 Union Find class
def __init__(self, n):
self.parents = list(range(n))
self.ranks = [0] * n
def find(self, i):
if self.parents[i] != i: self.parents[i] = self.find(self.parents[i])
return self.parents[i]
def merge(self, i, j):
ri, rj = self.find(i), self.find(j)
if ri != rj:
if self.ranks[ri] == self.ranks[rj]:
self.parents[ri] = rj
self.ranks[rj] += 1
elif self.ranks[ri] < self.ranks[rj]:
self.parents[ri] = rj
else:
self.parents[rj] = ri
class Solution:
def closedIsland(self, grid: List[List[int]]) -> int:
m = len(grid)
n = len(grid[0])
def map(r, c): return r * n + c # r*n+c로 현재 위치를 몇번째 위치에 있는지 변환
union_find = UnionFind(m * n)
island_count = 0
for r in range(m): # 일단 모든 island를 count
for c in range(n):
if grid[r][c] == 0:
island_count += 1
for ir, ic in [(0, 1), (1, 0), (-1, 0), (0, -1)]:
rr, cc = r + ir, c + ic
if 0 <= rr < m and 0 <= cc < n and grid[rr][cc] == 0:
if union_find.find(map(r, c)) != union_find.find(map(rr, cc)): #원래는 땅이 이어져있다면 parent가 같아야 하는데
island_count -= 1 # parent가 같지 않으면 island를 1개를 잘못 센거니까 빼줌.
union_find.merge(map(r, c), map(rr, cc)) # 둘의 parent를 같게 만들어줌.
open_islands = set() # edge에 잇는 island를 count
for r in range(m): # 맨 위쪽, 아래쪽 line의 land를 찾기
if grid[r][0] == 0:
open_islands.add(union_find.find(map(r, 0)))
if grid[r][n - 1] == 0:
open_islands.add(union_find.find(map(r, n - 1)))
for c in range(n): # 맨 오른쪽, 왼쪽 line의 land를 찾기
if grid[0][c] == 0:
open_islands.add(union_find.find(map(0, c)))
if grid[m - 1][c] == 0:
open_islands.add(union_find.find(map(m - 1, c)))
return island_count - len(open_islands) # 전체 land 갯수에서 edge에 있는 land갯수 빼기=> DFS보다는 비효율적인 방법이나 이렇게도 가능함을 알 수 있었다.
문제 링크
https://leetcode.com/problems/number-of-closed-islands/description/
Number of Closed Islands - LeetCode
Can you solve this real interview question? Number of Closed Islands - Given a 2D grid consists of 0s (land) and 1s (water). An island is a maximal 4-directionally connected group of 0s and a closed island is an island totally (all left, top, right,
leetcode.com
'코테 > LeetCode(Solve)' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [python3] 516. Longest Palindromic Subsequence (0) | 2023.04.14 |
|---|---|
| [python3] 71. Simplify Path (0) | 2023.04.12 |
| [python3] 2439. Minimize Maximum of Array (0) | 2023.04.05 |
| [python3] 2405. Optimal Partition of String (0) | 2023.04.04 |
| [python3] 881. Boats to Save People (0) | 2023.04.03 |




