| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | ||||
| 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
| 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 |
| 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 |
| 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 | 29 | 30 | 31 |
- Two Pointers
- heap
- stack
- Union Find
- hash table
- DailyLeetCoding
- Leedcode
- sorting
- Java
- Bellman-Ford
- leetcode
- 자료구조
- String
- Medium
- A* Algorithm
- python3
- VCS
- ArrayList vs LinkedList
- 광연자동차운전면허학원
- LinkedList
- dfs
- Hashtable
- Easy
- array
- greedy
- SinglyLinkedList
- hash
- 구현
- BFS
- graph
- Today
- Total
Min IT's Devlog
[python3] 1091. Shortest Path in Binary Matrix 본문
풀이 일자: 23.06.01
난이도: [Medium]
분류: [BFS]

문제 내용
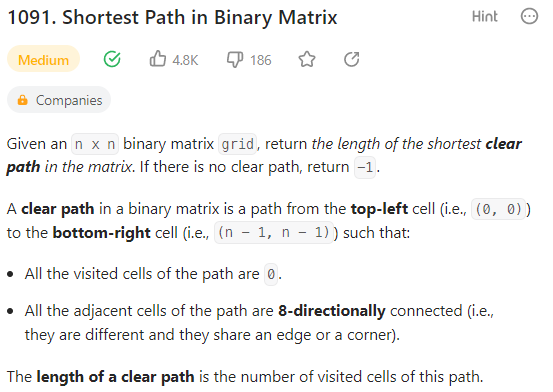
내용은 0과 1로 이루어진 배열이 주어졌을 때 (0,0)에서 (n-1,n-1)로 0만 밟으면서 이동할 때 최단 거리를 리턴하는 문제로 이동할 수 있는 범위는 edge와 맞닿아있는 총 8개의 면에 갈 수 있다.
문제 해결 흐름
1. 항상 이러한 배열과 최단거리의 조합은 BFS와 DFS 둘 중 하나를 떠올릴 수 있다.
→ 나는 BFS를 순회 알고리즘에서 매우 선호하기도 하고 DFS를 사용하기에는 BFS를 사용하는 것보다는 최단거리를 계산하기 부적합하다고 생각하여 BFS를 이용하여 문제를 해결했다.
class Solution:
def shortestPathBinaryMatrix(self, grid: List[List[int]]) -> int:
n = len(grid)
if grid[0][0] != 0 or grid[n-1][n-1] != 0:
return -1;
q = deque();
q.appendleft([0,0,1]);
ans = 0;
grid[0][0]=1;
while q:
x, y, length = q.pop();
if x==n-1 and y==n-1:
if ans == 0: ans = length
else: ans = min(ans, length)
else:
for i,j in [(x+1,y+1), (x+1,y), (x+1,y-1), (x,y+1), (x-1,y+1), (x-1,y-1), (x-1,y), (x,y-1)]:
if 0 <= i < n and 0 <= j < n:
if (grid[i][j]==0):
q.appendleft([i,j,length+1])
grid[i][j]=1;
return -1 if ans==0 else ans;기존에는 BFS의 visited를 이용하여 한번 이동한 곳으로는 이동하지 않도록 했으나 이러한 경우 TLE가 발생하게 된다. 이는 방문했는지를 탐지하기 위해 visited 배열을 순회할 때 시간이 많이 걸리는 것으로 보인다.
→ 물론 visited배열을 2차원 배열로 가져간다면 문제없을 것으로 보인다.
나는 이러한 방법 대신 아예 지나간 길을 1로 바꿔가면서 방문 여부를 표시했다.

Time Complexity: O(N^2)
BFS 순회이나 대각선 방향으로도 이동할 수 있기 때문에 (0,0)에서 (n-1,n-1)까지의 이동시 O(N)의 최적의 시간 복잡도를 가질 수 있으나 최악은 N^2에 가까울 것이다.
Space Complexity: O(N)
공간복잡도는 Queue로 인해 존재할 것이고 대략 N정도의 복잡도를 가지고 있다고 봐도 될 것이다.
다른 해결 방식
1. 가장 많은 vote를 받은 풀이는 Dijkstra알고리즘을 변형하여 만들어진 A*라는 최단 경로 검색 알고리즘을 사용한 풀이였다.
→ BFS로 푸는 것이 출제자의 의도였겠지만 지도 상에서의 최단 거리 계산, AI, 자율주행 분야에서 사용하는 등 다양한 곳에서 현실에서 사용되기 어려운 Dijkstra 알고리즘을 대체했기 때문에 충분히 idea정도 가져가볼 법한 풀이 방식이다. 시험기간이 끝나고 A* 알고리즘에 대해 포스팅을 해볼 생각이다.
class Solution:
def shortestPathBinaryMatrix(self, grid):
shortest_path = a_star_graph_search(
start = (0, 0),
goal_function = get_goal_function(grid),
successor_function = get_successor_function(grid),
heuristic = get_heuristic(grid)
)
if shortest_path is None or grid[0][0] == 1:
return -1
else:
return len(shortest_path);
return -1 if ans==0 else ans;
def a_star_graph_search(
start,
goal_function,
successor_function,
heuristic
):
visited = set()
came_from = dict()
distance = {start: 0}
frontier = PriorityQueue()
frontier.add(start)
while frontier:
node = frontier.pop()
if node in visited:
continue
if goal_function(node):
return reconstruct_path(came_from, start, node)
visited.add(node)
for successor in successor_function(node):
frontier.add(
successor,
priority = distance[node] + 1 + heuristic(successor)
)
if (successor not in distance
or distance[node] + 1 < distance[successor]):
distance[successor] = distance[node] + 1
came_from[successor] = node
return None
def reconstruct_path(came_from, start, end):
reverse_path = [end]
while end != start:
end = came_from[end]
reverse_path.append(end)
return list(reversed(reverse_path))
def get_goal_function(grid):
M = len(grid)
N = len(grid[0])
def is_bottom_right(cell):
return cell == (M-1, N-1)
return is_bottom_right
def get_successor_function(grid):
def get_clear_adjacent_cells(cell):
i, j = cell
return (
(i + a, j + b)
for a in (-1, 0, 1)
for b in (-1, 0, 1)
if a != 0 or b != 0
if 0 <= i + a < len(grid)
if 0 <= j + b < len(grid[0])
if grid[i + a][j + b] == 0
)
return get_clear_adjacent_cells
def get_heuristic(grid):
M, N = len(grid), len(grid[0])
(a, b) = goal_cell = (M - 1, N - 1)
def get_clear_path_distance_from_goal(cell):
(i, j) = cell
return max(abs(a - i), abs(b - j))
return get_clear_path_distance_from_goal
class PriorityQueue:
def __init__(self, iterable=[]):
self.heap = []
for value in iterable:
heappush(self.heap, (0, value))
def add(self, value, priority=0):
heappush(self.heap, (priority, value))
def pop(self):
priority, value = heappop(self.heap)
return value
def __len__(self):
return len(self.heap)
A* search in Python - Shortest Path in Binary Matrix - LeetCode
View lxnn's solution of Shortest Path in Binary Matrix on LeetCode, the world's largest programming community.
leetcode.com
문제 링크
https://leetcode.com/problems/shortest-path-in-binary-matrix/description/
Shortest Path in Binary Matrix - LeetCode
Can you solve this real interview question? Shortest Path in Binary Matrix - Given an n x n binary matrix grid, return the length of the shortest clear path in the matrix. If there is no clear path, return -1. A clear path in a binary matrix is a path from
leetcode.com
'코테 > LeetCode(Solve)' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [python3] 209. Minimum Size Subarray Sum (0) | 2023.07.06 |
|---|---|
| [python3] 859. Buddy Strings (0) | 2023.07.03 |
| [python3] 1396. Design Underground System (1) | 2023.05.31 |
| [python3] 347. Top K Frequent Elements (1) | 2023.05.22 |
| [python3] 785. Is Graph Bipartite? (1) | 2023.05.19 |




